Smithers' polymer consultants discuss the often overlooked reasons for premature failure in plastics and rubber products and the importance of systematic failure analysis when providing expert witness services.
What are the commercial implications of under-performing plastics and rubber products or components?
Expensive warranty claims, legal disputes and product recalls are some of the most serious consequences of an unexpected or premature failure of plastic and rubber products. Brand and market perception can also be adversely affected.
What are some of the most prevalent reasons for failure in plastics and rubber that you see?
Some common factors that are often overlooked and can therefore lead to failure include:
- Long-term behavior- rubber and plastics mechanical properties are both time and temperature dependent.
- Environmental effects - exposure to chemical environments and elevated temperature can reduce long term performance.
- Product manufacturing effects – errors in manufacturing polymer products can introduce complications that have a detrimental effect on the performance of the product.
How does ‘human factor’ contribute to the failure of plastic and rubber components?
The pie chart below shows 45% of the failures investigated by Smithers resulted from a poor material selection choice or a misunderstanding of the performance specification required for the product at its design stage. Failure to include all the material requirements in the selection process is a frequent cause of unsuitable usage later on.
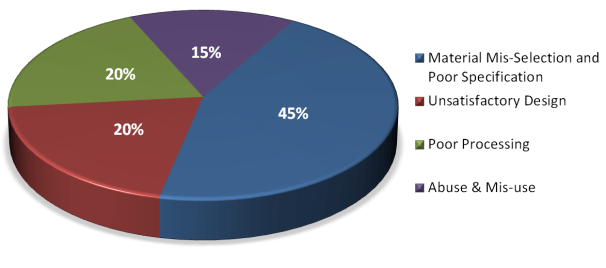
Rarely does an available material meet every requirement in a particular application but impartial assessments of the suitability of materials can help pre-empt that kind of product failure.

What are the main types of mechanical failure you encounter?
- Ductile failure is, by definition, failure at high strain. It is relatively straightforward to design plastic components to avoid this. However, in practice, ductile materials often fail in a brittle manner, which becomes much more difficult to predict.
- Brittle fracture is a low energy process characterised by failure at low strain, with little or no deformation. Components can contain small, crack-like defects which can act as stress concentration features; these micro-cracks grow under load and may eventually lead to rapid failure.
How do you investigate plastics and rubber failures at Smithers?
Our team of plastic and rubber consultants have access to a wide range of testing and polymer analysis tools at our UKAS accredited laboratories that enable us to reveal reasons for failure:
- Typical analysis on a failed product may require microscopic examination followed by chemical analysis to confirm material and additives type. We examine the polymer molecular distribution to determine material degradation status and thermal analysis to understand temperature transition responses. Comparative analysis would typically be conducted between the failed product and a new or as-good product in order to detect any potential differences in the material.
- A manufacturing process audit or design review may be appropriate to determine any influence on the cause of failure.
- Components or products are sometimes subjected to mechanical testing in creep or fatigue modes in specific operating environments to simulate in service conditions.
If plastic or rubber failure leads to a dispute or warranty claims how can expert witness services assist businesses with failure investigations?
Our experts are often called upon to support businesses at different stages of the dispute process, which may concern design flaws, incorrect manufacture and unexpected deterioration or misuse.
As part of our expert witness service we independently review the reasons for premature failure in plastics and rubber products. We provide robust in-depth technical capability – as well as experience – in the preparation and presentation of scientific and engineering evidence for court.
What accreditation does Smithers have for this work?
The laboratories at Smithers are UKAS ISO17025 accredited.
Find out more about our expert witness services and failure analysis services. We also offer plastics and rubber training courses led by expert tutors helping you gain a greater understanding around polymer technology.







