Hot-melt, water-based, solvent/reactive, and radiation-curing adhesives each play a crucial role in the performance of different packaging formats. In 2025, value in this segment is projected to reach $21.6 billion according to new research from Smithers, the global authority on the packaging industry. This will see a total of 7.2 million metric tonnes* of adhesives consumed in packaging construction.
The new market report,
The Future of Adhesives for Packaging to 2030, forecasts a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% will drive market value to $25.7 billion in 2030 (at constant prices). Consumption increases at a slower 3.2% CAGR to 8.4 million tonnes.
Across packaging the drive to improve sustainability is increasing. For adhesives this includes the development of more bio-derived ingredients, as well as solutions that allow brand owners to simplify designs or switch materials. In the EU the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR) 2025/40 will set design for recyclability criteria for all pack types – this will include consideration of adhesives selection, specifically.
Packaging is the largest segment in the broader adhesives industry, accounting for 40% of demand. The majority of adhesives are used with rigid paperboard packaging, for seaming/closing corrugated and cartonboard boxes; fabricating of cylindrical paperboard cores; as well as affixing labels and lidding stock to plastic, metal, and glass primary packs.
Of the four adhesive technologies examined in the Smithers study, water-based adhesives are the most widely used, at 52% of the global market. Hot-melt adhesives are the most lucrative packaging adhesive type, representing 35.2% of contemporary sales. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyolefins are the principal hot-melt formulations, continuing to displace less versatile styrene block copolymers chemistries.
Packaging converters also use more expensive polyamide, thermoplastic polyurethane hot melts in specialist applications. This segment has made the greatest progress in reducing dependency on petroleum-derived inputs. Multiple major suppliers now offer hot-melts with at least 25% bio-derived content, with some smaller suppliers offering up to 70%.
Solvent-borne and reactive adhesives continue to be pressured by sustainability concerns. Converters are switching to hot-melt or water-based adhesives where feasible; while the development of bio-derived ingredients has been slow. In 2025 they account for 17.8% of volume in the market, but have the worst growth outlook through to 2030.
Figure 1: Global packaging adhesives use, by pack format, 2020, 2025 & 2030 (million tonnes)
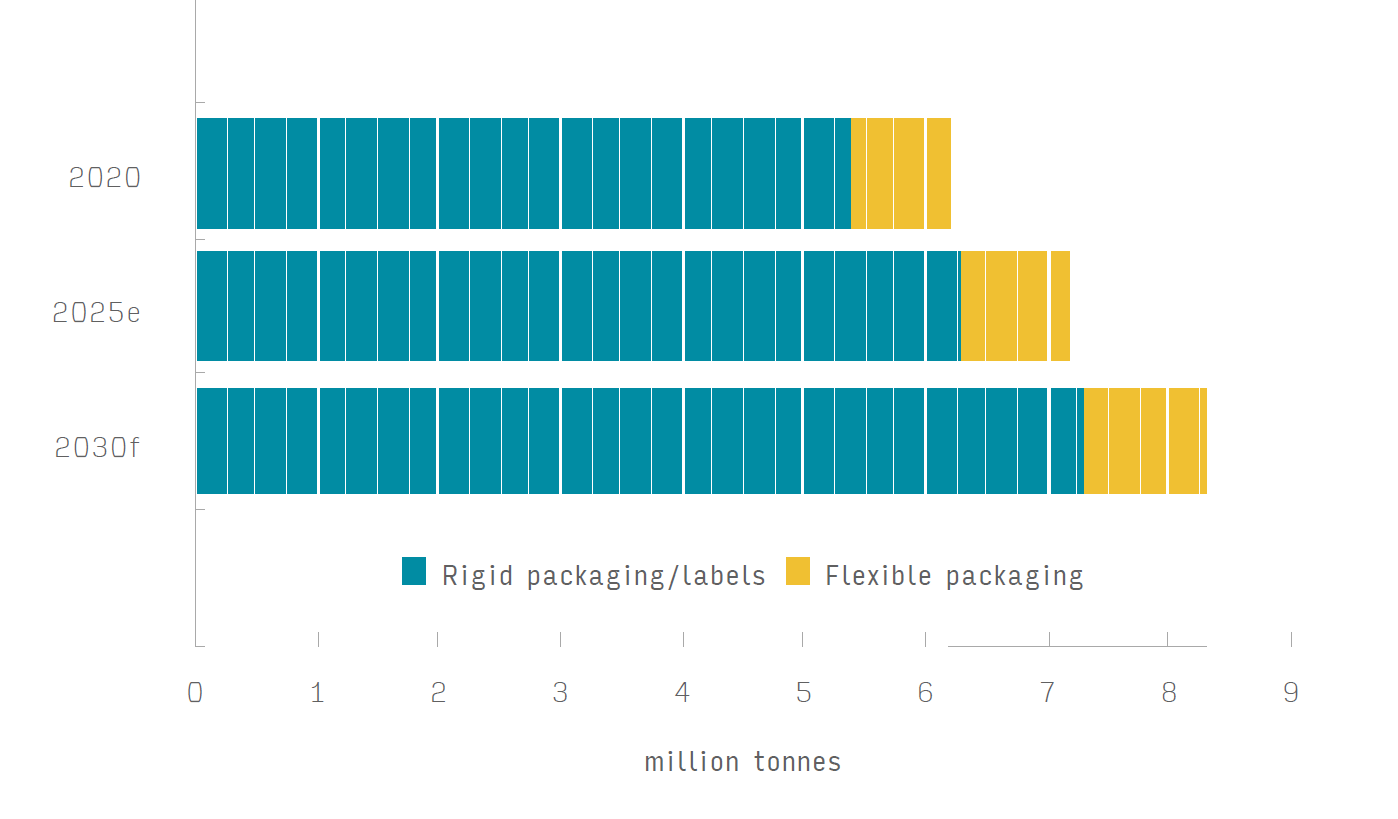
Source: Smithers
* Excludes thermoplastic tie-layers in flexible packaging, and adhesives used to laminate lines or facers in corrugated board construction.

